Prednisone
Pharmachologic effect
GKS. It has a pronounced anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic effect, has anti-shock and immunosuppressive activity. It affects various types of metabolism: increases blood glucose levels, has a catabolic effect, promotes redistribution of adipose tissue, can cause osteoporosis, causes a delay of sodium ions and water in the body, increases blood pressure. It affects the inflammatory process in the connective tissue and reduces the possibility of scar tissue formation.
Indications
Rheumatism, rheumatoid arthritis, dermatomyositis, periarteritis nodosa, scleroderma, ankylosing spondylitis. Bronchial asthma, allergic diseases. Addison's disease, acute adrenal insufficiency, adrenogenital syndrome. Hepatitis, hepatic coma, hypoglycemic states, lipoid nephrosis. Agranulocytosis, various forms of leukemia, lymphogranulomatosis, thrombocytopenic purpura, hemolytic anemia. Chorea. Pemphigus, eczema, pruritus, exfoliative dermatitis, psoriasis, pruritus, seborrheic dermatitis, lupus erythematosus, erythroderma, alopecia.
Dosing regimen
Individual. For adults, the initial dose is 20-30 mg / day, the maintenance dose is 5-10 mg / day. If necessary, the initial dose may be 15-100 mg / day, supporting - 5-15 mg / day. The daily dose should be reduced gradually. For children, the initial dose is 1-2 mg / kg / day in 4-6 doses, supporting - 300-600 mg / kg / day.
Side effect
On the part of the endocrine system: Itsenko-Cushing syndrome, weight gain, hyperglycemia, up to the development of steroid diabetes, depletion (up to atrophy) of the adrenal cortex, a negative nitrogen balance.
On the part of the digestive system: increased acidity of gastric juice, ulcerogenic effect on the gastrointestinal tract.

From the side of water and electrolyte balance: an increase in excretion of potassium, sodium retention in the body with the formation of edema.
Since the cardiovascular system: arterial hypertension.
From the musculoskeletal system: osteoporosis, aseptic necrosis of bones.
From the side of the central nervous system: mental disorders, steroid cataract, provoking latent glaucoma.
Other: reduced resistance to infections, delayed wound healing, increased blood clotting.
Contraindications
Peptic ulcer and duodenal ulcer in the acute phase, osteoporosis, Itsenko-Cushing's disease, tendency to thromboembolism, renal failure, severe arterial hypertension, systemic mycoses, viral infections, vaccination period, active tuberculosis, glaucoma, symptomatic symptomatics, inpidiation, psychotherapy, inpiduals, viral infections, vaccination, active symptomatic tuberculosis, glaucoma, symptomatic symptomatology, inpidiation, psychotherapy, inpiduals Hypersensitivity to prednisone.
Pregnancy and lactation
When pregnancy (especially in the first trimester) is used for health reasons.
Application for violations of kidney function
Contraindicated in renal failure.
Application for children
The use is possible according to the dosing regimen.
Special instructions
During treatment (especially long-term), it is necessary to observe an oculist, control of blood pressure and water-electrolyte balance, as well as pictures of peripheral blood and blood glucose levels; In order to reduce side effects, you can assign anabolic steroids, antibiotics, as well as increase potassium intake (diet, potassium supplements).
When indications for psoriasis in the history of prednisone in high doses prescribed under the strict supervision of a physician. In case of diabetes mellitus, it is prescribed only with absolute indications or for the prevention of the supposed insulin resistance. For non-specific infections, apply with caution and subject to simultaneous chemo-or antibiotic therapy. With latent forms of tuberculosis, prednisone can be used only in combination with anti-tuberculosis drugs.
In Addison's disease, concurrent use with barbiturates should be avoided.
After discontinuation of treatment, the onset of withdrawal syndrome, adrenal insufficiency, as well as exacerbation of the disease, for which prednisone was prescribed, may occur.
Inflammation
Protective and adaptive response of the body to the action of a pathogenic stimulus, manifested by the development at the site of damage to the tissue or organ changes in blood circulation and increased vascular permeability in combination with tissue dystrophy and cell proliferation.
The symptoms of inflammation are familiar to each of us: there is hardly a single person who has not had a burn or injury, an infectious disease, he never in his life rubbed his feet with uncomfortable shoes, did not freeze or dive so that water got into his ears.
Meanwhile, in all these situations, the development of the inflammatory process is possible:
- Inflammation of the eye - if it gets dust or you caught an infection.
- Inflammation of the appendages threatens women with hypothermia, etc.
What is inflammation? This is a kind of distress signal, the universal reaction of the body to damage or irritation of its tissues. Such a reaction is aimed at neutralizing the negative impact of damaging factors and restoring the normal work of the affected organs.
What is inflammation?
Inflammation is the response of the body to the fact that its cells are damaged or irritated. In response to this, he tries to get rid of the effects of the harmful effects and recover. When inflammation, pain can be very strong, because in this way the body signals a serious illness. What are the possible symptoms of inflammation besides pain?
- Redness of the skin (including caused by the expansion of capillaries).
- Swelling, swelling in anxiety zone.
- Local temperature increase (feeling of heat in a sore spot, while it occurs not necessarily with inflammation of the skin, but also with other inflammatory phenomena).
The chain of onset of symptoms is as follows: first, in the place where the damage or irritation of the cells occurs, the vessels dilate, due to which the blood flow becomes slower. The damaged area is poured with blood. The temperature in the area of inflammation rises. The walls of capillaries become more permeable, and through them leukocytes, macrophage cells and plasma penetrate into the surrounding tissues. There is local swelling and swelling that affect the nerve endings - they are impaired, causing an attack of inflammatory pain.
In the pathological process of inflammation are involved:
- Special proteins - inflammatory mediators (serotonin and cytokine).
- Macrophages - cells that capture and digest foreign proteins, bacteria, their own dead cells of the body.
- White blood cells (leukocytes) and lymphocytes.
- Cytokines are special molecules released onto the cell surface through which they interact with other cells (bradykinin, interleukin-1, an anti-inflammatory protein that causes decomposition of TNF tumors, kallidin).
- Proteins that affect the blood coagulation process.
Inflammation in women
Inflammation during pregnancy
Inflammation in women during pregnancy is associated with a decrease in immunity. What signs indicate pathology?
- Pains of varying intensity.
- Discharges having an unpleasant odor.
It should be remembered that acute inflammation of the genital area can cause irreparable damage to pregnancy:
- It causes anembryonic infection when an embryo does not form in the fetal egg.
- May contribute to embryo death and non-developing pregnancy.
- Possible spontaneous abortion or premature birth.
- Another likely complication is infection of the fetus in the womb, and even its death.
If a woman has chronic inflammation, it affects the immune system. At the same time, the endometrium tries to reject the embryo, perceiving it as something alien, and even if the embryo manages to consolidate, its location close to the cervix is bad for bearing.
Chronic inflammation of the ovaries leads to the formation of adhesions and proliferation of connective tissue, disrupts the cilia lining the tubes from the inside, reduces their lumen - all this increases the risk of ectopic pregnancy.
What is more dangerous chronic inflammation of the reproductive sphere? Immune failure contributes to the production of antibodies to their own tissues, and because of this, placental microthrombosis occurs, which leads to its detachment, abnormalities in the development of the fetus, gestosis.
How to avoid inflammatory complications during pregnancy?
- Warmly dressed, do not allow hypothermia.
- To observe personal hygiene, use special intimate cosmetics.
- Do not swim in questionable waters.
- Before the onset of pregnancy, it is necessary to cure the existing inflammation of the reproductive sphere.
Inflammation in nursing moms
Inflammation in women during breastfeeding is usually associated with milk stagnation (lactostasis) due to impaired patency of the breast ducts. An acute inflammatory process develops in the chest, and if infection with staphylococcus or streptococcus is added to this, infected mastitis is obtained. The situation is aggravated by improper attachment of the baby to the breast and injury to the nipples.
As a rule, inflammation in a woman develops rapidly:
- Suddenly, and to high numbers (39-40 &grad;C), the body temperature rises, the young mother is in a fever, she has a headache.
- Symptoms of inflammation of the mammary gland appear: severe pain, thickening is felt during palpation, the skin becomes hot to the touch, and hyperemic (red) areas may appear on it.
Mastitis requires urgent treatment, otherwise there is a risk of starting the disease and even losing part of the breast: complex cases end with the removal of the affected sector of the breast.
Should breastfeeding be stopped during treatment? Current recommendations of doctors boil down to the fact that the ban on HBV with mastitis is not justified. On the contrary, a diseased breast requires high-quality emptying, and the baby will do it better than any breast pump or manual decanting. If mastitis has taken a purulent form, it is necessary to express the milk before feeding until the pus is no longer exuding. However, specialist advice is required.
What can be treated young mother, so as not to harm the child? When a small stagnation appears, applying cool compresses from cabbage and curd will be helpful, but alcohol and warming ointments are not recommended. A warm shower can be used to improve the separation of milk from the breast and empty it as best as possible.
If the temperature continues to rise, and the pain in the chest increases, there is pus, you should immediately consult a doctor. Self-medication is unacceptable. Prescribe medication must doctor. In the absence of the effect of antibiotic therapy for two days, surgical assistance is required - puncture and pumping out of the pus or removal of the diseased area.
To prevent breast inflammation during breastfeeding, hygiene should be observed, comfortable underwear should be worn, and no milk stagnation should be allowed in the breast.
Inflammation in men
"Male" inflammation is a delicate topic. It is aggravated by the fact that men do not like to seek help from a doctor, they are pulled to the last, and as a result they get an appointment with an already fairly neglected disease. The following inflammatory diseases of the genital area are characteristic of men:
Prostatitis (inflammation of the prostate)
The most famous ailment, affecting many representatives of the fair sex. Inflammation of the gland occurs due to infection (bacterial, viral, fungal) or stagnation of prostate secretion or blood in it. Patients are concerned about the weak pain and unpleasant sensation in the perineum, difficulty urinating, discharge from the penis. Prostatitis without proper therapy can lead to male infertility. Treatment consists of prescribing antibiotics, a course of massage, physiotherapy, antispasmodics, and drugs to improve urine flow and prostate secretion.
Balanitis and balanoposthitis
Inflammation of the head and foreskin of the penis. Most often the child develops inflammation, especially if he has phimosis, but sometimes the disease occurs in adults. Patients are concerned about itching, redness and swelling of the head, pain, sometimes - lymph nodes in the groin increase. In the absence of proper treatment, the disease can be complicated by narrowing of the urethra, paraphimosis, sclerosing balanitis. The cause of the inflammation is a fungus or a pathogenic bacteria, infection from the urethra. The disease is treated with antibiotics and local antiseptics. If necessary, perform a surgical operation (circumcision).
Urethritis
Inflammation that affects the urethra. It is caused by the presence of genital infections. Much less likely to cause an allergy or injury. The main symptoms of urethritis are burning in the urethra, pain and pain when trying to urinate, purulent purulent-mucous discharge. The danger of inflammation is that the infection can reach the prostate, testicles, appendages, and even the kidneys in an upward way and lead to their diseases. Treatment of urethritis consists in prescribing antibiotics, immunomodulators, injecting drugs into the urethra, and in narrowing the urethra - expansion by means of special bougie.
Inflammation of the testicles and appendages
It is provoked by injuries and infectious diseases (mumps, scarlet fever, flu), but in most cases the infection comes from other organs of the genitourinary system. Inflammation begins from the acute stage, which is characterized by severe pain, an increase in the scrotum and skin tension on it, and a rise in temperature. Perhaps the development of a purulent process and blockage of ducts, fraught with sterility. If the disease is not treated, after 10-14 days it can turn into a chronic stage: the pain subsides, the temperature subsides, but palpation of the testicle will cause a painful mass. Antibiotic inflammation is treated, bed rest is required with the scrotum elevated. If necessary, surgery is performed (opening of the cavity and removal of pus, and in severe cases - removal of the testicle).
Inflammation in a child
Inflammation in newborns
Inflammation in a child in the neonatal period is a dangerous phenomenon, therefore a pediatrician must control it. What inflammatory diseases can overtake the baby, barely born?
Dacryocystitis - inflammation of the lacrimal sac, located between the nose and the inner corner of the eye.
It arises due to obstruction of the nasolacrimal canal due to the overgrowth of its lumen with the remains of embryonic tissue. The child manifests inflammation in purulent secretions, which are aggravated by pressure on the inner corner of the eye, reddening, relapses after the cancellation of antibiotics.
The treatment consists of two stages: conservative and surgical (used if the conservative did not help). The conservative method is a massage of the lacrimal sac to improve the outflow and patency of the channel, instillation of antibacterial drops into the eye. In the absence of the effect of such treatment, channeling is done. He is conducted by an ophthalmologist under local anesthesia. A probe is inserted into the lacrimal canal, and then the lacrimal duct is washed with an antiseptic. In addition, the baby is prescribed antibiotic eye drops, which need to be instilled a few days after sensing. For complete cure is usually enough one procedure.
Ear inflammation (otitis) is another scourge of newborns.
There are several reasons for the appearance of otitis. Toddlers cry a lot and mucus forms in the nasopharynx, which can clog the Eustachian tube. In addition, they often regurgitate excess milk after feeding, and this excess also contributes to pipe clogging. The anatomical structure of the Eustachian tubes of the baby also contributes to the development of inflammation: they are rather narrow and short, and the liquid easily clogs them.
Anxiety and cry, refusal to suck, fever is a sign of otitis in babies. Another symptom: if you put pressure on the tragus, the pain increases and the child worries more.
The treatment of ear inflammation in newborns has its own characteristics and should be carried out only under the supervision of a physician. If the eardrum is not damaged, ear drops and medicine shoes are allowed. To improve the outflow of fluid and relieve edema, the baby is prescribed vasoconstrictive drops. Sometimes it is possible to work on the Eustachian tube with the best effect with drops in the nose, and not in the ear.
Omphalitis (inflammation of the skin and fiber around the navel).
The navel of the newborn to complete healing is a large "entrance gate" for infection. Inflammation in this area is quite dangerous, because it can lead to the development of enterocolitis, lymphangitis, peritonitis and other serious complications. The cause of its occurrence is infection due to lack of hygiene, intrauterine infection or other diseases of the newborn.
Omphalitis is manifested by fever, anxiety or lethargy, a decrease in weight gain. Discharges appear from the umbilical wound, the skin around the skin becomes red and hot, and if blood vessels are involved in the inflammation, red stripes diverge from the navel. Omphalit can have four forms:
- catarrhal (slight redness, light discharge from the navel),
- purulent (discharge from the wound - purulent, the child has a slightly elevated temperature),
- phlegmonous (at the site of the umbilical wound - an ulcer in which pus accumulates, the baby feels bad, he has a high body temperature)
- necrotic - the most difficult when tissue necrosis occurs.
The treatment consists in treating the umbilical wound with antiseptics, with a purulent process, antibiotic ointments are applied, the wound is drained. Necrotic form is treated by excision of necrotic tissue. In addition, antibiotics are prescribed in the form of injections, vitamins, and in case of severe intoxication, intravenous injections of glucose.
Symptoms of inflammation
Pneumonia
Inflammation of the lungs (pneumonia) is a dangerous disease, which is an inflammation of the lung tissue. The causative agent of pneumonia can be bacteria, fungi and viruses. Sometimes it occurs for other reasons - for example, when the vessels are blocked with blood clots, the lung nutrition is disturbed, and so-called heart attack pneumonia occurs. Depending on the prevalence of the process, pneumonia can be focal, segmental, lobar and total (exciting all lung). When two lungs are affected, inflammation is called bilateral, and the disease of one lung is called unilateral pneumonia.
The symptoms of inflammation depend on the form of the disease. Classical bacterial pneumonia manifests itself
- high temperature
- strong cough with sputum
- shortness of breath.
There is an atypical course of the disease when the cough is weak and dry, and the patient is more worried about general malaise, headache and weakness.
Pneumonia is diagnosed by listening and tapping, chest X-ray, sputum analysis, general blood test and blood gas test.
Treatment of pneumonia depends on the cause that caused it: the bacterial form requires the prescription of antibiotics, the viral form requires antivirals, and the fungal form requires antifungal drugs. Since the causative agent of severe forms of bacterial pneumonia is Hemophilus bacillus and pneumococcus, vaccination is recommended (especially in risk groups - children, the elderly, weakened people).
Inflammation of the lymph nodes
Inflammation of the lymph nodes is due to a common or local infection, cancer, connective tissue diseases, injuries. Inflamed lymph nodes signal the body's fight against foreign proteins, bacteria, viruses, and its own altered cells. The increase in nodes in size means that the immune system has increased the number of lymphocytes produced to destroy proteins, bacteria, viruses and abnormal cells.
How does the lymph node inflammation manifest itself? Depending on the cause, which caused it, and the severity of the process, patients complain of
- fever and chills,
- headache and fatigue
- significant increase in lymph node size
- pain in them.
Reddened skin, discomfort when pressed around may indicate that suppuration has begun.
In a child, the inflammation of the lymph nodes in the head and neck is often accompanied by a cold.
Treatment of inflammation is the treatment of the underlying disease that caused it. If the lymph node has festered, antibiotics are prescribed (place in the form of ointment dressings and tablets inside), and if there is no effect, it is opened and drained.
Inflammation of the prostate gland
Inflammation of the prostate gland, or prostatitis, is a common male disease. The reason is infection in the genitals or congestion in the pelvis, which provokes a sedentary lifestyle, wearing tight underwear, reduced immunity, long sexual abstinence.
Inflammation of the gland is acute, and in the absence of proper treatment, the process becomes chronic. Complaints, which makes the patient, usually such: fever and chills, back pain, groin, lower abdomen. Sometimes pain occurs in the anus, perineum and scrotum. Men have difficulty urinating, there are false night desires to the toilet. Inflammation of the prostate gland can lead to male infertility.
It is necessary to treat prostatitis with the help of antibiotics, antipyretic and anti-inflammatory drugs, diuretic drugs, antispasmodics.
Nerve inflammation
Nerve inflammation is a pathology caused by trauma, impaired blood flow, infection, exposure to toxic substances and metabolic disorders.
Nerve inflammation can occur in two forms:
Neuralgia
Irritation of nerve fibers, which causes the patient to feel pain, tingling and numbness at the site of nerve damage, as well as when pressing. The skin in the area of the patient's nerve turns red or, on the contrary, becomes very pale. The most well-known variant of neuralgia is the defeat of the trigeminal nerve, when a person complains of severe short-term pain in one half of the face. The cause of this inflammation is infections, diseases of the sinuses of the nose and teeth, individual anatomical features (small openings of the skull in which nerves pass).
Neuritis
It is characterized by changes in the nerve itself (sheath, trunk). Symptoms are paralysis, paresis, trophic disorders, changes in sensitivity, if the optic nerves are stricken, the eyeball is still, the eyelids are drooping, the sight drops to complete blindness.
Treatment of nerve inflammation is directed to the cause that caused it: a bacterial injury is treated with antibiotics, and a viral one with antiviral drugs. If the nerve is inflamed due to injury, the diseased limb is immobilized. Violation associated with insufficient blood supply, requires the appointment of vasodilators. When neuralgia well help blockade the inflamed nerve. In all cases, medication is added to the treatment to reduce swelling and inflammation, painkillers, and vitamins of group B. After 12–14 days from the onset of the disease, anticholinesterase drugs and hyaluronidase preparations are prescribed. Massage and exercise therapy, physiotherapy (electrophoresis with lidaza or novocaine, UHF, impulse currents, etc.) also has a good effect.
Sometimes for the treatment of neuritis used surgical treatment: decompression, plastic surgery or stitching of damaged nerves. Neuralgia is treated by dissecting affected nerve endings and decompression.
Erysipelas
Erysipelas of the skin is an infectious disease that causes hemolytic streptococcus. The disease begins with symptoms of intoxication: nausea and vomiting, headache, temperature rise. Later, the skin begins to burn and "pull", it becomes hot, red spots and swelling appear, with bullae form - bubbles with liquid contents. Lymph nodes are enlarged, lymphatic vessels are inflamed.
Treatment of erysipelas consists of taking antibiotics for which hemolytic streptococcus is sensitive. Additionally, ultraviolet irradiation of the skin and laser therapy can be prescribed.
Gum disease
Gum disease occurs in many people. Symptoms of the disease are redness and swelling of the gums, putrid breath, pain and bleeding of the gums. The last sign is difficult not to notice: as a rule, blood oozes out when you brush your teeth or bite hard food. Pain is sometimes taken by patients for toothache, but when examining a periodontist, it turns out that the gum is still sore.
Gum disease has three degrees:
Gingivitis
The easiest form, which is expressed by redness and bleeding gums. The cause of inflammation is poor hygiene and the lack of a full-fledged chewing load on the teeth. Treatment at this stage consists of proper teeth brushing, regular professional care, and training of teeth and gums by chewing solid foods.
Periodontitis
Inflammation of the gums of moderate severity. Bad breath from the mouth, swelling and pain are added to the red bleeding gums, pockets appear between the teeth and gums where food remains are clogged, and disease-causing microbes multiply there. The cause of periodontitis may be improper prosthetics, gastrointestinal diseases and other common diseases, lack of proper hygiene. The treatment of inflammation, in addition to eliminating the cause of its occurrence, consists in therapeutic procedures: special medications are placed in the periodontal pockets.
Periodontal disease
The third and most severe degree of inflammation. Here, inflammation affects the tissue of the tooth and the bone beneath it, which causes teeth to loose, and then fall out. Treatment of periodontal disease is carried out in different ways: remove tartar, sanitize the periodontal pockets, make injections into the gums, perform splinting (attaching a loose tooth to stable adjacent teeth).
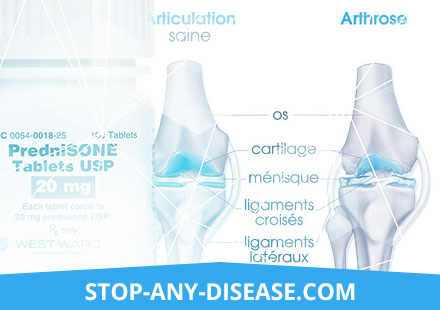
Inflammation of the joints
Doctors call arthritis inflammation of the joints (if one joint is affected, it is monoarthritis, if there are several - polyarthritis). Pathology begins with inflammation of the inner articular sac, and then spreads to the cartilage and the heads of the bones, tendons and ligaments, the tissues surrounding the joint.
The causes of arthritis are many: it can be injuries, infections, autoimmune diseases, and allergies. Symptoms of inflammation in joints include:
- Pains of varying intensity.
- Redness and swelling.
- Local temperature increase in the area of the affected joint.
- Increase the size of the joint.
- Limited mobility.
Arthritis treatment is aimed at eliminating the cause of inflammation. Good effect gives physiotherapy, intra-articular injections of hormonal drugs, anti-inflammatory therapy.
Inflammation of the appendages
Inflammation of the appendages is a process that affects the fallopian tubes and ovaries. In medical practice, such inflammation is called salpingoophoritis. It occurs when pathogenic microbes enter the tubes and ovaries. Salpingo-oophoritis may be acute or chronic. Patients complain of pain in the lower abdomen and groin, aggravated at the end of the chicle before menstruation, discomfort during intercourse and decreased libido, fever (with an acute course or exacerbation of the chronic process), weakness and tiredness.
Inflammation of the appendages is dangerous because it can lead to female infertility, so women pay close attention to its treatment. Depending on the severity of the process, salpingo-oophoritis is treated with antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, mud applications, physiotherapy (electrophoresis, ozone therapy, etc.). Good effect gives a sanatorium and resort recovery. If the disease does not respond to therapy and the diagnosis is in doubt, resort to therapeutic and diagnostic laparoscopy.
Inflammation of the gallbladder
Inflammation of the gallbladder (cholecystitis) can be without a stone and on the background of gallstone disease. Stagnation of bile due to violations of the outflow, stone trauma to the walls, the formation of pressure sores - all this leads to inflammation of the bladder.
The main symptom of cholecystitis is pain of varying intensity. It can be very strong and short-term with biliary colic or weak, aching, but constant. In addition, patients may be disturbed.
- itchy skin
- feeling of bitterness in the mouth
- upset stool.
The best way to get rid of the inflammation of the bladder is considered to be its surgical removal (in the presence of stones in the gallbladder). Coneless cholecystitis is treated conservatively. The most gentle method of removal is laparoscopic, it is used during surgery without an acute condition. If the gallbladder needs to be removed in the midst of acute cholecystitis, surgeons prefer laparotomic intervention.
Ovarian inflammation
Inflammation of the ovaries is called Otoritis. The cause of the pathological process is penetration into the reproductive organs of pathogenic bacteria and microorganisms. The course of the disease can be acute, subacute and chronic. In the case of acute inflammation, pains in the lower abdomen, fever, are disturbed, while palpation, there is tension and soreness in the lower abdomen. Subacute and chronic inflammation is manifested by aching pain in the groin, menstrual disorders, general malaise.
Oorit and salpingo-oophoritis in the acute stage are treated mainly with antibiotics, and physiotherapy is added in the subacute stage. In the chronic process, the whole arsenal of means is used: antibiotics during exacerbation, physiotherapy, mud therapy, immunostimulants, sanatorium-resort treatment, vitamins.
Ear infection
Ear inflammation (otitis) can be external, medium and internal. The reason in all three cases, one - the ingress of microbes or fungus, sometimes - an allergy.
External otitis is an inflammatory process in the auricle, the symptoms of which are edema, itching, and fluid discharge. Sometimes external otitis is manifested by an abscess located inside the auricle.
Internal otitis is a deep inflammation of the inner ear, which is expressed by tinnitus, vomiting and nausea. Patients feel dizzy, suffer a sense of balance.
The most common type of ear inflammation is otitis media. It begins with tolerable pain, which gradually increases and becomes acute. Sometimes body temperature rises. The pus accumulated in the ear pushes against the eardrum, can break through it and go out - in this case, the patient immediately experiences relief.
The treatment of ear inflammation depends on the form in which it proceeds. For the treatment of external otitis, ointments are enough, and if there is an abscess in the auricle, alcohol-induced lotions will help. With otitis media, local anesthetics and antibiotics, turunda with boric alcohol, vasoconstrictor nasal drops are prescribed. Inflammation of the inner ear requires hospitalization of the patient, bed rest, detoxification therapy and antibiotics.
Inflammation of the ear is considered by many to be a non-serious disease, with which it is not necessary to consult a doctor - and for good reason. The fact is that the wrong treatment can lead to sad consequences up to deafness, especially if we are talking about internal otitis. Therefore, it is better to entrust the treatment to the doctor.
Skin inflammation
Inflammation of the skin can take different forms:
- Dermatitis of different origin (contact, seborrheic, allergic)
- Purulent inflammation (boils, carbuncles, abscesses)
- Psoriasis
- Eczema
- Erysipelas
Symptoms of the inflammatory process are different: boils, carbuncles and abscesses cause severe pain when pressed, the skin around the center of education becomes red and hot. Eczema is characterized by burning and itching. Dermatitis occurs with the appearance of blisters, edema, severe redness.
Treatment depends on the type of inflammation. Purulent processes are treated with antibiotic ointment dressings, if necessary, the formation is opened surgically. In psoriasis, local treatment is prescribed in the form of ointments, sometimes psychotropic drugs. Dermatitis of allergic origin and eczema are treated with sedatives, hormone-based ointments, naphthalan, etc.
Eye inflammation
Inflammation of the eye has several forms, it can be both acute and chronic. What types of inflammatory eye diseases are most common?
Conjunctivitis
Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye (conjunctiva) due to infection or allergies. Conjunctivitis can be acute or chronic. Symptoms of inflammation are expressed quite clearly - swelling and redness of the conjunctiva, tears, fear of light, redness of the eye protein, and in the case of a purulent process - discharge of pus from the eye. Conjunctivitis is treated based on its form: bacterial - with antibiotics, viral - with antiviral drops, an “artificial tear” preparation, and antiviral tablets. Allergic form of conjunctivitis requires limiting contact with the allergen and the appointment of antihistamine eye drops. If they do not help, you can use hormone-based drops.
Uveitis
Inflammation of the choroid. The most dangerous form is inflammation of the iris and ciliary body of the eye. For uveitis characterized by photophobia, redness of the eyes, blurred vision. Self-treatment is strictly contraindicated: an urgent need to contact an ophthalmologist, because the disease threatens to be completely blind. Uveitis therapy consists of prescribing painkillers and preparations for dilating the pupil (atropine), anti-inflammatory drugs and antibiotics.
Barley
Acute purulent inflammation of the eye (ciliary follicle or sebaceous gland next to the follicle). It is manifested by redness, pain with pressure, and in the case of a large size of barley - at rest, puffiness. After a few days, a yellow “head” appears, which is then opened and outflow of pus occurs. In most cases, the cause of the disease is Staphylococcus aureus. For the appointment of treatment should contact an ophthalmologist. As a rule, ointments or drops with an antibiotic are prescribed; when the temperature rises, antibiotic pills are taken orally. Sometimes when forming an abscess, the help of a surgeon is needed - he opens it and removes pus.
Halyazion
Chronic inflammatory process affecting cartilage and sebaceous gland at the edge of the eyelid. It is a formation similar to barley in both appearance and symptoms, but differs from it in a relapsing course. Chalazion is first treated conservatively (with drops, ointments, injection of steroids), and in the absence of effect, the formation is surgically removed.
Pain in inflammation
Pain during inflammation is a signal of distress to the body. It is caused by irritation of the nerve endings with special substances (inflammatory mediators), irritation of the endings due to swelling and swelling, changes in pH and osmotic pressure, imbalance of calcium and potassium ions. At the same time, one thing is closely connected with the other: from inflammation, the pain increases, and from pain, the production of inflammatory mediators increases.
The nature of pain with inflammation changes over time. If you burn your hand, the pain is initially unbearable and acute. Over time, it decreases, but at the same time it becomes more common: it can already hurt not only in the place of the burn, but also intact skin around. Why it happens? The reason is inflammation. The burn provokes the formation of mediators of the inflammatory process, and they contribute to the expansion of capillaries and more abundant blood flow, because of which there is a feeling of warmth and the skin turns red. Due to the excessive release of mediators, the sensitivity of neurons increases so much that even a simple touch on the skin near the burn causes unpleasant sensations. It turns out that pain provokes inflammation, and it causes increased pain. Therefore, for the best effect, along with the treatment of the inflammatory process, you need to pay attention to high-quality anesthesia.
Causes of inflammation
There are only two reasons for inflammation:
- Damage to the cells.
- Exposure to stimuli of any kind.
But the circumstances in which there is contact with irritants and damaged cells, much more:
- Mechanical injury resulting from shock, friction, compression.
- Thermal or chemical burns.
- Frostbite
- Electric shock.
- All sorts of microorganisms - pathogens. Depending on the type of germs, inflammation can occur in different forms. The most acute form is suppuration.
In medicine, there is a classification of inflammations by causes:
- Infectious-inflammatory process is caused by microbes that have invaded the tissues: anaerobic ones provoke putrefactive inflammation, and aerobic ones - purulent. Infectious inflammation can be acute and chronic.
- Toxic inflammation occurs due to the destruction of the body's cells by harmful substances.
- The autoimmune process is associated with a pathology of immunity in which the body begins to produce antibodies against its own healthy tissues. These antibodies damage tissues and cause the development of inflammation.
- Purulent septic inflammation
- Paraneoplastic syndrome occurs in cancer patients due to the fact that organs and systems react to the presence of a tumor and the release of biologically active substances by it. As a result, a person develops symptoms similar to, for example, rheumatic lesions or scleroderma (consolidation of connective tissues).
- Traumatic and post-traumatic inflammation - any injury is accompanied by a reaction of the body, manifested by pain, swelling and restriction of the functions of the damaged organ or part of the body. So, inflammation of the joints after impact or compression leads to the development of post-traumatic arthritis, which causes severe pain, stiffness, crunch and swelling in the area of damage.
Diagnosis of inflammation
History taking
Diagnostic procedures for suspected inflammation begin with anamnesis. The doctor finds out from the patient all the circumstances in which he had pain, how they developed, what is troubling at the moment. Inspection and history taking is the main tool for the initial diagnosis of inflammation. As a rule, doctors are interested in:
Anamnesis of a person's life - what chronic diseases does he have, were there any operations, injuries, what kind of living and social conditions does a person live in. Such information is very important - for example, when diagnosing erysipelas, the doctor needs to know whether the patient has had this before, if he has diabetes, skin fungus, or immune disorders.
Anamnesis of the disease - how it started, how it is developing at the moment, whether a person applied for medical help, what treatment was prescribed, how it worked. For example, if a patient is worried about inflammation of the joints, you need to find out why it happened (whether there was an injury or a blow), what was expressed - did the limb flex, become swollen, reddened, than and how the patient was treated independently before going to hospital .
Epidemiological history is important in the diagnosis of infectious-inflammatory process. The doctor is interested in whether the patient has contacted infectious diseases, whether there have been trips to epidemiologically unfavorable countries or areas, and if it is an intestinal infection, what and where he ate.
If we are talking about inflammation in women in the reproductive sphere, the gynecological history is collected: what were the diseases and gynecology operations, abortion, the nature of the menstrual cycle, etc., before.
Family history - the presence of cases of the same disease in the blood relatives, whether there are hereditary diseases in the family and how many people they have affected. Family history suggests that a person has one or another pathology - for example, if there are cases of celiac disease in the family (genetically determined chronic inflammation of the small intestine with impaired food digestion), the likelihood of developing the disease increases.
An allergic history provides an opportunity to establish the presence of inflammation characteristic of allergies. Interviewing the patient, the doctor finds out if the person has a reaction to food, plants, drugs, vaccinations, how it manifests itself, what drugs are removed.
A nutritional history is relevant when it comes to inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract, gallbladder and biliary tract. Here the doctor is interested in the regimen and diet of the patient - how many times a day, what food he eats, in what quantity.
Laboratory research methods
Laboratory tests provide an opportunity to determine the presence of inflammation and clarify its nature. What research is needed to diagnose the inflammatory process?
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)
Universal marker of acute inflammation, in which there are changes in the blood. The procedure of analysis is as follows: blood is filled with a tube with an anticoagulant, and then it is left vertically for an hour. During this time, the red blood cells fall to the bottom of the tube, and the plasma remains at the top. The unit of measurement of ESR is millimeters per hour, that is, how many millimeters of a layer of deposited red blood cells formed in one hour at the bottom of the tube. When the blood is changed under the influence of an acute inflammatory process, the globulins and fibrinogens in its composition envelop the erythrocytes, they stick together with each other and fall down. The more acute the inflammation, the more such agglomerated erythrocytes settle to the bottom. It turns out that a high rate of ESR demonstrates the presence of acute inflammation.
From the erythrocyte sedimentation rate, it is impossible to understand which organ is affected by the pathological process. In addition, ESR - non-specific analysis: the indicator can grow not only with inflammation (elevated levels can occur during pregnancy, anemia, use of certain drugs, and even against the background of complete health, it is usually higher in women than in men). Sometimes it happens that inflammation occurs without any increase in ESR.
Considering all this, other laboratory tests are used for diagnosis in conjunction with the determination of ESR - for example, they analyze the C-reactive protein.
C-reactive protein (CRP) indicates an acute phase of inflammation and appears in the blood within a few hours after the onset of the pathological process.
Protein is synthesized by the liver, which receives information about the need to increase its production from macrophages (cells responsible for digestion of foreign cells, microbes, toxins, and own dead cells). CRP is determined by serum. The peculiarity of this protein is a short half-life (from half a day to a day), therefore, by its fluctuations, one can quickly judge the effectiveness of the treatment started: if CRP decreases, it means that therapy has the desired effect.
CRP is a more specific analysis compared to ESR. It does not depend on many indicators. which affect the fluctuation of ESR. In addition, ESR responds to an increase or, conversely, a decrease in the intensity of the inflammatory process much slower than CRP.
There are other markers of inflammatory processes, but because of the relatively high cost in mass diagnostics, they are used less frequently:
- Haptoglobin is a plasma protein responsible for the binding of hemoglobin. Increasing its level indicates the presence of acute inflammation.
- Antistreptolysin - indicates acute acute streptococcal infection and the presence of rheumatism or glomerulonephritis.
- Rheumatoid factor - an indicator of rheumatoid arthritis, autoimmune diseases, chronic inflammation. The analysis shows the presence of immunoglobulin antibodies that destroy tissue.
In addition to specific markers of inflammation, other laboratory tests are used in the diagnosis:
Complete blood count with leukocyte formula - the changes in the proportions and the number of leukocytes of different types can be judged on the presence of an inflammatory process. Thus, a significant increase in neutrophil levels suggests acute bacterial inflammation.
Sometimes a biochemical blood test is useful - for some types of inflammation, the main indicators change. For example, when pancreatitis increases the level of amylase, lipase, trypsin. Sometimes an increase in blood glucose indirectly indicates inflammation of the pancreas.
Urinalysis: the appearance of mucus and leukocytes in it is an indicator of the inflammatory process. If red blood cell counts after scarlet fever show up, this may indicate the development of glomerulonephritis, a chronic inflammatory disease of the kidneys.
Coprogram (feces analysis) helps diagnose inflammation in the intestines: it is indicated by the presence of mucus, epithelium and undigested food, the presence of leukocytes and iodophilic (iodine-colored) flora.
When it is necessary to determine gynecological inflammation in women, laboratory tests of vaginal secretions and smears from the cervix, urethra and cervix come to the aid of the doctor. Occasionally, endometrium is collected from the uterus. The study helps to determine the presence of the inflammatory process, the presence of pathogenic microflora, infectious agents.
"Male" inflammation (prostatitis, urethritis, balanoposthitis, etc.) helps to determine the bacteriological seeding of prostate juice, a smear on genital infections.
For the diagnosis of the inflammatory process in the lungs using a common analysis of sputum. The number, color, appearance, presence of certain cells and fibers can be judged on the presence of bronchitis, pneumonia, tuberculosis, purulent damage to the lungs.
By smear and bacteriological culture of the nasopharynx, inflammation in this area can be determined. For example, in often sick children, the Epstein-Barr virus, which is responsible for persistent colds and the development of infectious mononucleosis, is usually sown. Mononucleosis is accompanied by high fever, damage to the spleen, inflammation and an increase in lymph nodes.
Instrumental research methods
To diagnose the inflammatory process, it is useful to conduct instrumental studies. What are the main types of research?
Radiology (X-ray, CT (MSCT - a type of CT))
One of the most common methods of instrumental diagnosis of inflammation. What is its advantage? It attracts patients with a lack of pain and quickness of execution, and doctors like X-ray, MRI and MSCT for good informativity: you can see a diseased organ in a properly taken picture, determine how inflamed it is, whether the inflammation affected the surrounding organs. This method is quite accurate - especially MRI and MSCT, where the image of the internal organs is recorded in layers in increments of several millimeters. With the help of X-rays, MRI and MSCT, inflammation of the pelvic organs, abdomen, chest, limbs and joints can be diagnosed.
Endoscopy
Examination of internal organs by means of a special optical device (endoscope) inserted through natural holes or punctures. Endoscopic examination is good because it allows the doctor to see the surface of the organs in multiple magnification, determine the presence of inflamed areas of the mucosa, and if necessary, make a biopsy of the suspicious area. What are the types of endoscopic diagnostics? If pulmonary inflammation is suspected, tuberculosis or bronchitis is performed bronchoscopy, fibrogastroduodenoscopy and colonoscopy are used to diagnose inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract; Laparoscopic endoscopy is used to diagnose inflammation in the abdominal cavity.
Ultrasound procedure
Modern ultrasound helps to see the inflammation of the lymph nodes, joints, gallbladder, changes in the liver, kidneys, suggest inflammatory diseases of the female genital sphere.
Functional diagnostics
Allows you to identify a violation in the work of an organ or system. For example, if you suspect pneumonia or asthma, peak flowmetry is used (indicates the maximum rate of exhalation of a person), spirometry (estimates the volume and rate of exhalation).
Treatment of inflammation
Medication use
For the treatment of inflammation using several groups of medicines:
Antibiotics are prescribed if the bacterial nature of the pathology is proven.
This can be done using a special analysis - sowing with the determination of drug sensitivity, when the material is placed in a nutrient medium and waiting for the growth of bacteria, and then check which of the antibiotics kills the grown colonies most quickly. The more precisely and more quickly antibiotics are prescribed, the greater the chances that the disease will be cured quickly and without consequences. Antibiotic treatment requires erysipelas of the skin, inflammation of the lungs of bacterial origin, neglected inflammation of the ovaries and all diseases for which rapid reproduction of microbes with negative consequences for the patient is possible.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are lowering body temperature drugs that have analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects.
They inhibit the production of a special enzyme cyclooxygenase, which interferes with the production of prostaglandins (they affect the development of inflammation). NSAIDs are prescribed to reduce the severity of the inflammatory process, anesthetize and reduce the temperature.
Antihistamines - as the name implies, they suppress the production of histamine in the body.
Histamine is a substance that regulates the transmission of nerve impulses between cells. It can provoke a spasm of large vessels, expansion and increase of capillary permeability, smooth muscle spasm, adrenaline rush, increased secretion of digestive enzymes and mucus in the bronchi. Usually antihistamines are prescribed for allergic inflammation and as a means to relieve symptoms during a cold.
Hormones are an emergency remedy, which is used only for severe inflammation due to the fact that it has contraindications and serious side effects.
The action of hormones is to counteract the production of prostaglandins, block the enzymes that destroy cells, reduce the permeability of the walls of blood vessels and inhibit the formation of exudate and proliferation of connective tissue in the area of inflammation.
Physiotherapy for inflammation
Physical therapy is usually used to treat inflammation in the convalescent stage or chronic disease. Depending on the type of pathology, you can apply different types of physiotherapy treatment:
- Electrophoresis (administration of drugs using electric current).
- Pulsed electric current therapy (diadynamic therapy) is used to treat nerve inflammation.
- Cryotherapy (cold treatment) - local and general.
- Laser therapy - its effect is based on the favorable effect of light emission with one fixed wavelength.
- Ultrasound therapy - the effect is based on the effects of ultrasound, which accelerates the process of tissue regeneration, resorption of edema, restores nerve conduction, eliminates spasm. Ultrasound therapy has a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect.
- Mud therapy is a method of physiotherapy, which is mainly used to treat gynecological inflammation in women. Mud has a strong anti-inflammatory effect, stimulates the immune system, improves blood flow in the area of application of mud applications.
Treatment of acute inflammation
Depending on the cause of the inflammation, the treatment of the acute form can be surgical and conservative. Conservative therapy is the appointment of:
- Antibiotics.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
- If necessary - antihistamine drugs.
- If the inflammation is very active, and other drugs do not help very well - a short course of hormones (mainly used in autoimmune and allergic processes).
It is necessary to direct all forces to the treatment of the acute stage of inflammation, because:
- Possible development of complications that are life-threatening.
- Untimely or poor quality therapy can lead to the process becoming chronic, with frequent exacerbations.
Surgical treatment of inflammation is required when it is not possible to cope in a conservative way. This usually happens in acute cholecystitis, gynecological diseases, appendicitis, purulent inflammations of cellulose (phlegmon) and abscesses.
Treatment of chronic inflammation
The causes of inflammation may be different. Sometimes it is provoked by chronic infection or other chronic diseases. In this case, the inflammation lasts a long time, is constantly repeated and exacerbated. Treat him surgically and conservatively. Conservative treatment includes taking medication, physiotherapy, physiotherapy, and balneological procedures. Surgical methods are used when they are expected to have a more impressive effect than conservative therapy, and a radical cure for the patient. Operations try to be carried out beyond the acute stage in order to reduce possible negative consequences.
What types of chronic inflammation are common, and how are they treated?
Pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract organs - appendicitis, pancreatitis, colitis, etc.
The method of treatment depends on the specific disease - so, with pancreatitis, a starvation diet, enzymes, painkillers, antioxidants and toxins are first prescribed, and in the absence of an effect, a surgical removal of a part of the gland is performed. Appendicitis is usually treated surgically at once, since patients come with acute pain, and the source of inflammation must be removed as soon as possible.
Inflammation of the biliary system (liver, biliary tract and bladder) - most often manifested by cholecystitis.
Paceless non-suppurative cholecystitis is treated conservatively. In the presence of stones, surgical removal of the gallbladder is often used, and in the acute stage, doctors prefer laparotomic surgery, and more gentle laparoscopy is possible without an exacerbation.
Chronic inflammation of the eye (eyelid) due to clogging of the sebaceous gland - chalazion.
Treatment begins conservatively, prescribing injections of hormones into the cavity of the chalazion, eye drops, ointments. If this does not help, the formation is surgically removed on an outpatient basis.
Chronic inflammation of the urinary system (pyelonephritis, cystitis, urethritis)
Requires the appointment of local antiseptics (uroseptikov), proper drinking regime, drugs to improve blood circulation in the kidneys.
Chronic inflammation of the gynecological sphere
They cure by increasing general and local immunity, antibiotics and antimicrobial agents, physiotherapy (ozone therapy and mud therapy helps well). If a woman has symptoms of sluggish inflammation of the ovaries, uterus, tubes, but the usual methods did not succeed in accurately detecting the disease, the patient can be given a diagnostic and at the same time therapeutic laparoscopy, during which the diagnosis will be made and surgical treatment will be carried out (dissection of adhesions, ovarian resection, recovery cross pipes).
Surgical treatment methods
There are cases when the treatment of inflammation is impossible without surgery. As a rule, acute diseases lead to the patient's operating table, and medical assistance should be provided immediately:
Acute cholecystitis is an inflammatory process in the gallbladder that affects its walls.
Surgery to remove the gallbladder is carried out in the presence of stones and the lack of effect of conservative therapy. Inflammation of the bladder occurs due to the violation of the outflow of bile and its infection with pathogenic bacteria. Late treatment of cholecystitis can lead to serious complications when the pathological process captures the surrounding fiber or leads to gangrene of the bladder. Surgical care is to remove the diseased organ.
Acute inflammation of the pancreas - acute pancreatitis.
Severe inflammation of the gland can be fatal. Surgical treatment of pancreatitis is to remove the inflammatory tissues of the gland with the ineffectiveness of conservative treatment.
Appendicitis
Acute inflammation of the appendix of the cecum, which is currently being treated with laparoscopic surgery: the appendix is removed with instruments that are inserted through small punctures, under the control of a video camera.
Lymph node purulent inflammation (lymphadenitis)
Also requires surgical treatment - suppuration is opened, drained, and then antibiotics are prescribed.
Gynecological diseases: acute purulent inflammation of the appendages, ovaries
The reason for the emergency operation, because the rupture of organs and the spread of purulent process in the abdominal cavity threatens the life of a woman.
Purulent diseases of the skin and tissues: boils, abscesses, cellulitis (spilled inflammation of fiber without clear localization).
In this case, the surgeon opens the lesion, cleans the cavity from pus, puts drainage, and then the patient is prescribed antibiotic treatment.
Acute inflammation of ENT organs: otitis, sinusitis, ethmoiditis, etc.
The essence of all operations in this case is to ensure the outflow of purulent contents from the closed cavities to the outside. So, if a patient has purulent ear inflammation, the eardrum is incised. In the case of acute ethmoiditis and abscess formation, the cells of the bone grid are opened, and pus is removed.
Pathology of the oral cavity - this includes the treatment of periodontitis, inflammation of the periosteum, osteomyelitis, inflammation of the salivary glands.
Prevention of inflammation
Prevention of inflammatory diseases may be different:
Increasing the overall immunity is always necessary, regardless of what kind of inflammation in question. Due to their strong immunity, pathogens can not reproduce when ingested.
In order not to get pneumonia, it is necessary to promptly treat acute respiratory viral infections, not to overcool, and if a person is at risk for pneumococcal infections and diseases caused by hemophilus bacilli, he is shown prophylactic vaccination. The risk group includes patients with immune diseases, chronic lung and cardiovascular diseases, the elderly (especially those who live in boarding schools) and patients who need hemodialysis.
For the prevention of inflammation of the skin of various types (erysipelas, boils, abscesses), you need to properly maintain personal hygiene: take a shower daily, use pH-neutral detergents. It is very important to avoid the occurrence of wounds, grazes and diaper rash, and if they do appear, skin should be treated with antiseptics. They damage the skin and sunburns, damaging the upper protective layer and reducing immunity - therefore, they should be treated without fail (panthenol-based preparations are well helpful). Since erysipelas usually occurs on the background of chronic diseases, attention should be paid to their treatment: diabetes, thrombophlebitis, trophic ulcers, endocrine diseases require close monitoring. To improve blood circulation and lymph flow, it is recommended to take massage courses twice a year.
For the prevention of inflammatory diseases of the gallbladder and biliary tract, it is necessary to follow a reasonable diet with a restriction of animal fats, fried and cold foods, an increase in the proportion of fiber in the diet and fractional food intake. Such a diet prevents the formation of stones and the appearance of gallstone disease, which is often the cause of bladder inflammation.
Prevention of acute pancreatitis is in compliance with the principles of healthy eating, rejection of bad habits, healthy lifestyle.
To avoid inflammation of the gums and oral cavity, it is necessary to observe hygiene, timely treat teeth, use rinses and good toothpastes.
Prevention of appendicitis is based on the fight against stool disorder and other disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, preventing infection in the body. This can be achieved proper nutrition with a high content of fiber, the establishment of a diet. Hygiene will also help - washing vegetables, fruits, berries, washing hands thoroughly before eating.
Inflammatory diseases of the female genital tract (inflammation of the appendages, ovaries, vagina and cervix) can be avoided by avoiding casual sexual relationships, protecting themselves from infections, abandoning abortions in favor of civilized contraceptives. In order not to "limp" local immunity, it is important not to supercool. Hygiene is also required - regular showers, rejection of daily pads, it is desirable to use detergents for intimate hygiene.
Inflammation of the joints can be avoided if you exercise, to monitor your posture, to prevent injuries and excessive load, to monitor your weight.
Since acute inflammation of the lymph nodes usually occurs when they are injured or injured, traumatic situations need to be avoided. If the lymph nodes are inflamed because of any chronic infection, you should fight it - because while it is there, the inflammation will recur.
Inflammation can occur in any organ, and this is not surprising: an inflammatory reaction is the option of protecting the body from damaging or pathogenic effects on it. The body itself gives a distress signal, to which it is necessary to respond in a timely manner, otherwise the untreated disease becomes chronic, and is exacerbated by time after time.
The cause of inflammation can be not only a disease, but also an injury: physical, chemical, thermal. Sometimes even the sun is guilty of indisposition - from excessively long stay under its rays, the skin becomes inflamed and reddened.
Treat inflammation in different ways depending on what causes it. Treatment may be surgical (surgery) or conservative (tablets, ointments, physiotherapy, massage, injections). The specific plan of procedures in each case is determined by the doctor, based on the results of the examination. It is not only senseless to engage in self-medication for inflammation, but it is also dangerous — without proper experience and qualifications, it is impossible to establish the diagnosis accurately and prescribe competent therapy to oneself. As a result, you are wasting your valuable time, and you risk getting serious complications. Therefore, we must remember: any inflammation is a reason for an urgent appeal to a doctor!
Allergic diseases of workers occupy a prominent place in the statistics of occupational pathology
In connection with the widespread introduction of chemical technologies in production, the organization of plants producing protein concentrates and additives, the development of the pharmaceutical industry, etc. the number of patients suffering from allergic diseases associated with a particular production has increased. True, cases of the occurrence of bronchial asthma in millers, workers of fur and leather industries, woodworking plants have long been known.
The influence of production conditions on the occurrence of the disease, the pathogenesis of the disease and its clinical picture in each individual case may be different, however, in each production the development of an allergic disease has its own characteristics.
Contact dermatitis
Most often, dermatitis occurs in individuals working with formalin, chromium, mercury, turpentine, antibiotics, glue, dyes. The clinical course of contact dermatitis is characterized at the onset of the disease by a lesion of the skin itself - hyperemia and edema. Later, symptoms of damage to the deeper layers of the skin appear - bubbles form, which burst, weeping yellow scabs appear, that is, eczematization occurs. With the appearance of large drain bubbles with a large area of hyperemia, even I or II degree burns can be assumed.
In some people, dermatitis immediately takes a papular-infiltrative character with severe itching, with sharply limited edges. In the chronic phase of the disease, the clinical picture is no different from non-professional contact dermatitis, it can only be a location, i.e., damage to those skin areas that are exposed to aggressive hazards (hands, face and other exposed parts of the body). Often, such dermatitis is accompanied by lesions of the mucous membranes of the eyes, nose, and mouth.
There are also edematous manifestations on the eyelids, dyshidrosis of the palms and soles. The features of professional contact dermatitis are sudden onset and frequent recurrence when resuming work. In the future, due to persistent itching, scratching and superinfection occur, and with continued exposure of the allergen due to its spread through the affected skin in a lymphohematogenous way, general symptoms such as fever, malaise, weakness, etc. may occur.
According to the clinical picture of contact dermatitis, it is not always possible to solve the question of how allergen it is caused, since allergens of a different nature can cause the same clinical manifestations. Issues of etiological diagnosis in professional dermatitis are very relevant, but skin tests in such patients can not always be carried out because of the danger of causing exacerbation. Detection of antibodies is also not possible, since they lack free-circulating antibodies, therefore, a properly collected history, data on the course of the disease and the presence of an elimination factor are sometimes crucial for a correct diagnosis.
The prognosis for professional contact dermatitis is favorable - with timely diagnosis, elimination of occupational hazards (transfer to another job), and proper treatment. True, quite often, despite all the measures, dermatitis, having arisen on the basis of occupational hazards, can continue and full recovery does not occur. This indicates the existence of complicating factors (other chronic diseases, polyvalence, superinfection, improper treatment).
Prevention is based on general and individual means of protection when dealing with occupational hazards. In addition to these measures, it is necessary to avoid working in chemically and biologically harmful industries for people with a predisposition to allergies, with skin dysfunction. It is also desirable to preliminarily determine the suitability of the person to work with a particular substance - carrying out an appropriate test.
Cropped mushrooms and eritema
Much less common professional urticaria. Causes of urticaria and erythema can be chemical, physical and biological.
Chemical causes most often cause urticaria and erythema in people associated with the pharmaceutical industry, nurses, pharmacy workers. There are cases of urticaria for morphine, arnica, ipecac, mercury preparations, penicillin, novocaine, phenol, ammonia, and also for herbal remedies — thuja, rhododendron, nettle, tobacco, and oils; for biological products - tetanus toxoid, anti-influenza vaccines, etc.
Of the physical factors that cause urticaria and erythema, the effect of high and low temperature should be called. Employees of ceramic factories, steel-smelting shops often have extensive erythema and urticaria for high temperatures, and for traffic police officers - for low temperatures. The biological factors causing urticaria and erythema include dust, animal dander (veterinarians), insect bites (lumberjacks, beekeepers), contact with fish, jellyfish (ichthyologists, fishermen), etc.
Bronchial asthma
Bronchial asthma associated with occupational hazards is heterogeneous. A. E. VERMEL (1966) identifies 3 groups of occupational bronchial asthma:
- caused by sensitizing substances (primary asthma);
- caused by substances that irritate the local respiratory tract, leading to chronic bronchitis and only then to bronchial asthma (secondary asthma);
- caused by sensitizers, at the same time having a local irritant effect.
Occupational bronchial asthma occurs when dust, smoke, and vapors of various substances are inhaled. Very rarely, bronchial asthma occurs when the ingress of harmful substances through the gastrointestinal tract during the tasting of cheeses, coffee, tea, wine, etc.
Occupational asthma has some distinctive features depending on the nature of production hazards. At various times from the beginning of contact with occupational hazards, a first attack of asthma may occur.
Sometimes bronchial asthma occurs in people without any other manifestations of allergy, but more often it is combined with the presence of eczema, dermatitis, rhinitis, angioedema, etc.
Asthma attacks occur at different times, but more often at work, at the end of a shift, after some exposure to an industrial allergen.
At the beginning of the disease, asthma attacks are not heavy, are removed if you leave the production room, but over time the attacks become harder, suffer from coughing attacks with the separation of thick viscous sputum. Later, seizures are caused by other factors, excitement, weather changes, etc.
In cases where occupational asthma does not occur as a primary disease, but against the background of a chronic pathological process in a bronchopulmonary apparatus (silicosis, pneumoconiosis, bronchitis), the period to the development of typical attacks is rather long.
Asthmatic phenomena develop in these patients gradually, against the background of previous bronchitis, persistent cough. In cases of secondary asthma, it is difficult to establish a connection with occupational hazards, since seizures occur outside of work, during holidays, etc. In these cases, primary chemical or mechanical damage to the bronchial mucosa leads to the development of occupational bronchitis, on the basis of which bronchial asthma develops, often an infectious-allergic form.
Exogenous allergic alveoli
It is especially necessary to single out a group of diseases associated with damage to the lung tissue by immune mechanisms under the action of exogenous allergens - spores of fungi, protein antigens. Since exogenous allergic alveolitis is associated with the inhalation of certain professional allergens, they are named according to the profession, for example, “farmer's lung”, “lung of furriers”, “lung of coffee threshers”, “lung of pigeon breeders”, etc.
Currently, there are more than 20 professions in which exogenous alveolitis occurs, which are based on immunological mechanisms (the reaction "allergen - antibody").
A feature of these mechanisms is the formation of precipitating antibodies, which, when combined with an allergen, form immune complexes that settle in the walls of the alveoli, small bronchi. The deposition of immune complexes contributes to the increased permeability of the vascular wall. During the course of allergic exogenous alveolitis, all 3 types of allergic reactions can be traced (see Chap. 2).
People who are predisposed to allergic reactions get sick with exogenous pulmonary alveolitis after prolonged contact with an allergen. The course of the disease can be acute, subacute and chronic. Sometimes alveolitis occurs periodically in the form of acute outbreaks when inhalation of large doses of the allergen (cleaning of the pigeon house, bulkhead, hay, work on the mill).
In the acute form, the disease is often interpreted as pneumonia, as there is an abundance of physical data (wheezing, moist, finely bubbly), increased ESR, and leukocytosis.
In the course of the disease, irreversible changes occur in the lung tissue associated with the formation of granulomas and scarring, which lead to the development of pulmonary fibrosis.
In the acute and subacute stages, the use of glucocorticoid hormones is indicated. Prevention is to prevent contact of patients with the appropriate allergen (change of profession). The chronic form of exogenous allergic alveolitis is difficult to treat, and symptomatic therapy is usually performed.
 US
US AU
AU CA
CA DE
DE FR
FR IT
IT ES
ES




